eResearch Australasia 2023 Conference
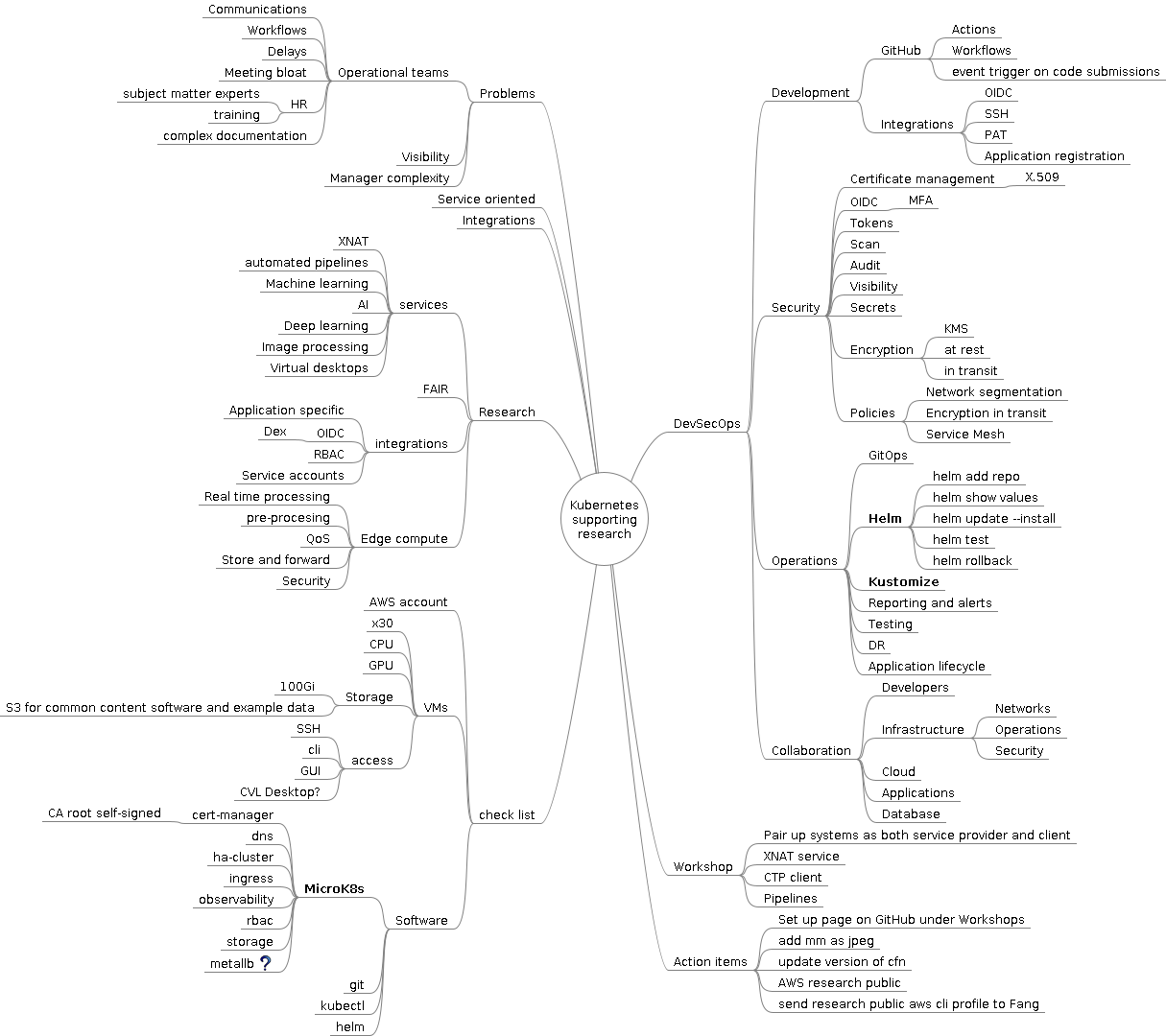
Introduction
Terms and concepts from our perspective
- Kubernetes
- Cloud
- Simple - really meaning
managed complexity
Very brief Kubernetes at high level
- Kubernetes Components
- Control plane
- API server
- etcd
- Node components
- kubelet - makes sure that containers are running in a Pod
- kube-proxy - network proxy that runs on each node
- Container runtime - run containers
- CRI - Container Runtime Interface
- e.g., containerd
- Control plane
Minimum host machine specs
- Recommendation: use the VM provided by the instructor. This will help to ensure the machine has been tested to work with the content.
| min. spec | |
|---|---|
| RAM | 8 Gi |
| vCPU | 2 |
| HDD | 100 GB |
Notes for instructors
- Print out the details bellow and distribute to attendees to speed up setup
- Machine DNS or IP address for connection
- Password set up for workshop
- Quick Start guide outlining how to connect and access the GUI. Both Windows and Mac clients should be included as a minimum.
- Verify cloud resource is available to support ec2 instance numbers
aws service-quotas get-service-quota --service-code ec2 --quota-code L-3819A6DF- NB: Measured in vCPUs - g4dn.xlarge - 4x vCPU ea - 4x 24 participants = 96 vCPUs
- Verify access to VM using password from the workshop location to ensure unhindered access
Design highlights
Getting started
Your instructor will provide the following
- AWS EC2 instance
- DNS address to host
- Initial password to the default
ubuntuuser account
ssh -Llocalhost:63389:localhost:3389 ubuntu@MACHINE_NAME.ap-southeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com
tmux
# Install Kubernetes
sudo snap install microk8s --classic
sudo usermod -a -G microk8s ubuntu
# Add client tools
sudo snap install kubectl --classic
echo 'source <(kubectl completion bash)' >>~/.bashrc
sudo snap install helm --classic
echo 'source <(helm completion bash)' >>~/.bashrc
mkdir -p $HOME/.local/bin
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
# calicoctl
curl -L https://github.com/projectcalico/calico/releases/download/v3.25.0/calicoctl-linux-amd64 -o $HOME/.local/bin/calicoctl
chmod +x $HOME/.local/bin/calicoctl
# Log out and back in
# This will load all the environment changes into your new active shell.
# Setup kubectl with microk8s cluster configuration
(umask 0077; microk8s config > $HOME/.kube/config)
# Whats happened
microk8s status
kubectl get nodes
kubectl get pod --all-namespaces
# Notice Calico virutal network interfaces
ip addr
# View default Calico IP pod address allocation pool
calicoctl get ippool
Getting to know your Kubernetes cluster
kubectl version
kubectl cluster-info dump |less
kubectl api-resources
Internal DNS
# The default namespace 'default' is used if namespace is not specified
kubectl run testmachine --image=ubuntu:latest -- tail -f /dev/null
kubectl get pod
kubectl exec -it testmachine -- bash
# In the container shell
# Internal cluster DNS configuration
cat /etc/resolv.conf
# Kubernetes as a process watchdog (systemd) NB: PID 1
ps aux
apt update
apt -y install dnsutils
dig google.com.au
Covered
- Microk8s basics
- Kubernetes cluster overview
- Internal DNS and service naming convention
- Getting adhoc development and testing pods
Kubernetes add-ons
Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
microk8s enable rbac
kubectl api-resources
Observability
microk8s enable observability
kubectl --namespace observability get pods -l "release=kube-prom-stack"
kubectl port-forward service/kube-prom-stack-grafana 8080:80
# Using the browser
# Address: http://localhost:8080
# Username: admin
# Password: prom-operator
Persistence, Storage classes, Volumes
microk8s enable hostpath-storage
kubectl get sc
cat <<EOT |kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: my-first-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
storageClassName: microk8s-hostpath
EOT
kubectl get pvc
kubectl descibe pvc my-first-pvc
Create a PVC consumer
cat <<EOT |kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-first-pod
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: my-first-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: basic-web
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: http-web-svc
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/www/html
name: my-first-pvc
volumes:
- name: my-first-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: my-first-pvc
EOT
watch kubectl get pod
kubectl describe pod my-first-pod
kubectl logs my-first-pod
kubectl get pvc,pv
NB extra details for later:
- Label and selectors
- container ports
Services, Ingress and Load balancers
microk8s enable ingress
kubectl get pod --all-namespaces
kubectl api-resources
kubectl get ingressclasses
curl localhost:80
Add a HTTP service to ‘my-first-pod’
cat <<EOT |kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-first-service
spec:
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: my-first-pod
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
EOT
kubectl port-forward service/my-first-service 8080:80
# Open another terminal
curl localhost:8080
Add an Ingress to ‘my-first-pod’
cat <<EOT |kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-first-ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: "mywebservice.local"
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: my-first-service
port:
number: 80
EOT
kubectl get ing
curl --resolve mywebservice.local:80:127.0.0.1 http://mywebservice.local
Deploy applications using Helm
Install AIS XNAT
# Add the AIS helm repository
helm repo add ais https://australian-imaging-service.github.io/charts
helm repo update
helm search repo ais/
# Review and create local values.yaml for deployment
helm show values ais/xnat |less
HOST=$(hostname --fqdn)
XNATDCMNodePort=30002
cat <<EOT >xnat-values.yaml
global:
storageClass: microk8s-hostpath
postgresql:
enabled: true
xnat-web:
image:
repository: ghcr.io/australian-imaging-service/xnat
tag: v1.8.9.1
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 8000Mi
limits:
cpu: 4000m
memory: 8000Mi
nonheapmem: 4000Mi
dicom_scp:
recievers:
- ae_title: "XNAT"
port: 8104
nodePort: $XNATDCMNodePort
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-connect-timeout: "150"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "100"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "100"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffers-number: "4"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: "32k"
hosts:
- host: $HOST
plugins:
ohif-viewer: {}
probes:
startup:
failureThreshold: 15
periodSeconds: 60
liveness:
failureThreshold: 12
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
readiness:
failureThreshold: 1
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 3
replicaCount: 1
EOT
helm upgrade xnat ais/xnat -n xnat -i --create-namespace -f xnat-values.yaml
# Watch pods and ingres creation
watch -n 1 -d kubectl get pods,ing -n xnat
Testig XNAT
For Mac users, need to install Microsoft Remote Desktop from Apple App store
Add a new PC in Microsoft Remote Desktop
PC Name: localhost:63389
User account: ubuntu
Connect to your VM
Run Firefox and access http://dummy-xnat-domain-name
Log in as user 'admin' with password 'admin'
X.509 certificate management
microk8s enable cert-manager
cat <<EOT |kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
metadata:
name: selfsign
spec:
selfSigned: {}
EOT
Mapping it out